In recent years, sustainable design has shifted from a trend to a necessity in architecture, interior design, and urban planning. As awareness about environmental issues grows, the importance of creating spaces that are not only functional but also eco-friendly has become more evident. Sustainable design is about creating buildings and environments that minimize environmental impact, reduce waste, and promote long-term sustainability.
In this blog, we’ll explore the principles of sustainable design, its benefits, and the innovative strategies and trends that are shaping the future of eco-friendly architecture. Whether you’re building a new home, retrofitting an office, or designing a public space, sustainable design practices can help you contribute to a healthier planet.
What is Sustainable Design?
Sustainable design refers to the process of creating products, buildings, and environments that meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It focuses on reducing environmental impact by using energy-efficient materials, minimizing waste, conserving water, and lowering carbon footprints.
The core concept of sustainable design is to create spaces that are in harmony with the natural environment. This can be achieved through thoughtful choices of materials, construction methods, energy use, and even the way spaces are used over time. Sustainable design is an integrated approach that takes the environment, social impact, and economic feasibility into account.
Principles of Sustainable Design:
- Energy Efficiency: One of the fundamental pillars of sustainable design is energy efficiency. By designing buildings and spaces that reduce energy consumption, we can lessen the burden on natural resources and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Passive Design Strategies: Incorporating design elements like proper insulation, natural ventilation, and maximizing natural daylight can reduce the need for artificial heating, cooling, and lighting.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Using renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems can significantly reduce a building’s carbon footprint and reliance on nonrenewable energy sources.
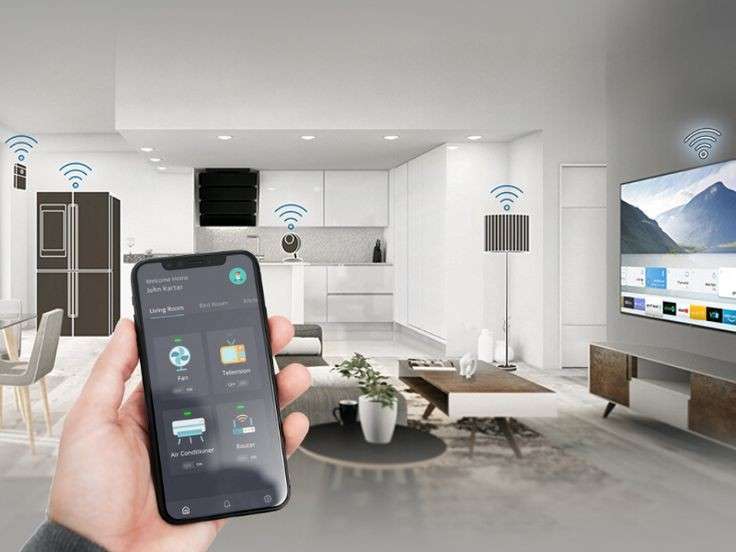
- Smart Technology: Integrating smart thermostats, energy-efficient lighting, and energy management systems allows for better control of energy usage.
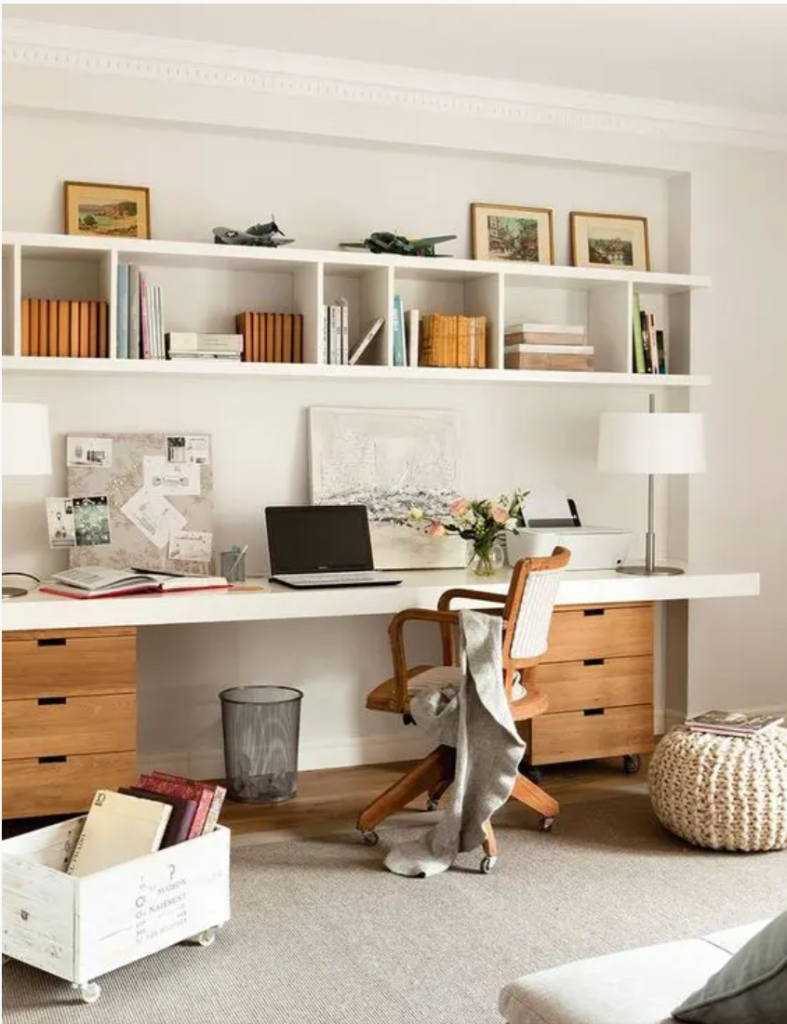
- Use of Sustainable Materials: Sustainable design prioritizes the use of materials that have minimal environmental impact and can be reused or recycled. This not only helps reduce the need for virgin resources but also supports a circular economy.
- Locally Sourced Materials: Using materials sourced close to the project site reduces the environmental impact associated with transportation.
- Recycled and Upcycled Materials: Materials like reclaimed wood, recycled glass, and steel can be repurposed for new construction, reducing waste and conserving resources.
- Low-Impact Materials: Choosing materials with low environmental impact—such as bamboo, cork, or responsibly sourced timber—reduces deforestation and other harmful practices associated with construction.